CVPR 2020 detection paper explanations
Published:
Detection in Crowded Scenes: One Proposal Multiple Predictions
This source paper propose a new type of bounding box pruning technique called set-nms . Conventional nms (non-maximum suppression) over-kills predictions in highly overlapped objects. Because nms is not a learned process of pruning boxes. This paper proposes a model which predicts multiple instance at once, more specifically two boxes at once and after ward set-nms box pruning is used which outputs final selected boxes. The head of faster rcnn model is changed from one instance prediction (class+location) to two instance predictions (2 class + 2 locations). The prediction other than instances is assigned as a dummy background. Figure 2 shows the equation for predicting K instances at once.
Model and Loss function:
This paper shows the best suited value of K=2 which means its predicts two boxes where each box is defined by location and corresponding class.

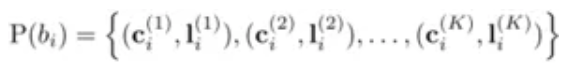
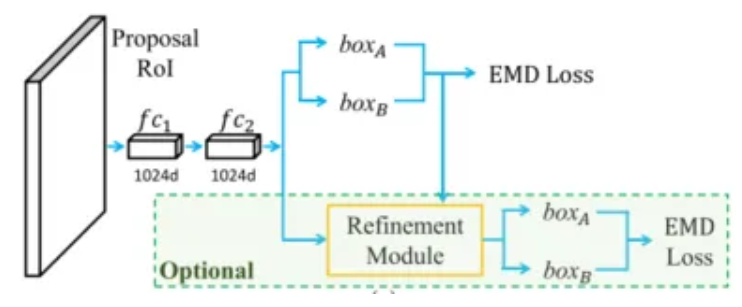
Earth Mover’s distance (EMD) loss: This paper use earth mover’s distance as a loss function with K=2. However they use faster rcnn (cross entropy+regression) function in loss, we explain the concept of EMD loss here. Lets say, {4,1,8} are ground truth and {7,2,5} is their corresponding predictions consecutively (shown in fig 4.). For sake of simplicity we use absolute sum error as loss function. Then earth mover’s distance loss will be the minimum loss between ground truth and different combination of predictions. It means prediction order doesn’t matter in earth mover’s distance. In object detection earth mover’s loss function (cross entropy and regression), the order (ground truth and prediction boxes) which provides minimum loss is considered as loss value.

Set-NMS: The proposed model outputs a tensor of shape = N * K * 6, where N is the number of proposal prediction, K is number prediction per proposal and [x1,y1,x2,y2,score,class] represents 6 in the shape. This model basically predicts N number of box pairs (K=2). Initially, they use a threshold to remove very low scoring boxes and then apply set-nms on rest of the boxes. This threshold helps to remove some dummy background boxes from the predictions. The paper use a little customised nms which is suitable to prune boxes from predictions. In their ideal set-up of K=2, If two boxes comes from same pair nms doesn’t remove the boxes, boxes are only removed by nms if those are comes from different pairs.
